Static stretching (SS) has formed parts of regular training, recovery, physiotherapy, pre-match warm-ups and cool-downs for years. It is often thought that static stretching can help:
Research suggests that other forms of training such as strength training can achieve these effects just as effectively if not more effectively than static stretching.
There is consistent evidence that SS increases flexibility in the short-term, although the gains in flexibility decrease relatively quickly, such that they are lost within 30 minutes!1,2 There is also evidence to suggest that prolonged static stretching performed regularly over several weeks can result in meaningful improvements in range of motion (ROM).3,4
However, the same can be said for strength training where flexibility is also increased by, especially eccentric training. The magnitude of increase achieved appears to be close to that achieved through static stretching. Strength training also seems to increase muscle mass, bone mass, strength, decreased risk of falls and other benefits.5, 6
Many recent studies and reviews have reported that sustained static stretching before performance either reduces max strength, power, plyometric ability, balance and agility or has no effect on performance.7, 8 It also seems that the longer the sustained static stretch the greater the negative impact is on performance.8
So what about its effects on endurance performance? Well, stretching doesn’t seem to improve running or walking efficiency. Direct impact on endurance performance is uncertain with stretching whereas strength training has been shown to consistently improve endurance.9, 10
Several studies have suggested that decreased flexibility at baseline of injury or stretching less often, may predispose to injury. However, many recent studies have struggled to find any relationship between static stretching and injury prevention. Several systematic reviews have concluded that there is not enough evidence to either support or discontinue the use of stretching for injury prevention.11, 12
Other forms of training and treatments seem to consistently show to reduce injury rates with Laursen et al mentioning that “consistently favourable estimates were obtained for all injury prevention measures except for stretching.” 13 This study showed that progressive strength training reduced injury rates to less than a third!
In terms of making the recovery process quicker, studies have shown that performing static stretching for 2x a day reduces time until return to sport by around 2 days or longer.14 In contrast an eccentric strengthening program out performed a traditional program with a mix of static stretching, concentric and eccentric exercises, with return to sport being 23 days less!
Absolutely! It seems that static stretching helps improve flexibility both in the short and long term and can be a lot more easily tolerated in the acute phases of injury and more accessible to a lot of people. However, it seems that there are other ways in which we can improve flexibility, such as eccentric strengthening which proposes other benefits aside from just flexibility. When it comes to improvements in performance it is unclear if there are any positive effects. There is evidence to suggest that prolonged static stretching before activities can hinder performance and should be avoided before explosive activities and substituted for a more active warm-up. In the long term, effects on performance are equivocal whereas strength training has been shown to improve performance. It also seems that static stretching has minimal effect on injury prevention in contrast to strength training typically involving an eccentric component where injury and time returning to sport is reduced.
My view? Use stretching as a form of training when flexibility is the goal you’re working towards or is specifically needed for your activity/sport such as gymnastics or dancing. That being said, it shouldn’t make up the bulk of your program and you should look to implement strength training over stretching in the majority of cases.

Blog
Balance is a crucial component of overall health and wellness as it plays a vital role in various aspects of daily life, physical activities, and overall well-being.
Blog
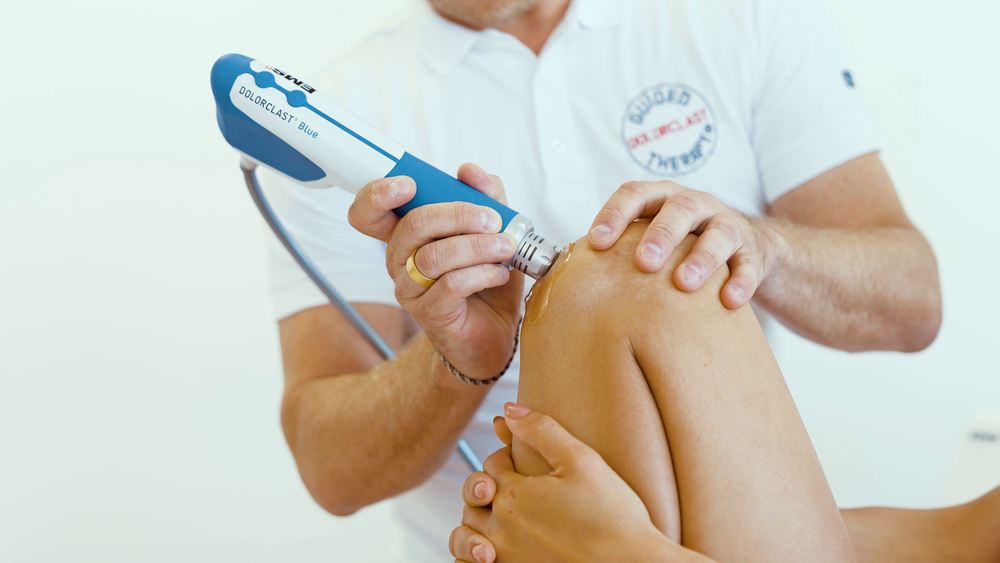
Nikos takes a look at how Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) stands out as a revolutionary treatment and has transformed how Physiotherapists approach various musculoskeletal conditions.

Are you ready to have a chat with our team to discover how we can help you achieve a better quality of health, fitness and well-being?
Book an appointment with our team and start the journey to creating the perfect treatment plan for your issue, your lifestyle and your
goals.